|
|
| Laser Materials Processing Division |
Pulsed Laser Deposition
Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD) is a versatile and perhaps one of the simplest growth techniques to deposit high quality films and nanostructures of myriad of materials ranging from superconductors to semiconductors to dielectrics to metals and many more under optimized conditions. The technique uses high power (typically ~108 W/cm-2) laser pulses to melt and/or vaporize materials from their high density targets due to an ablation process. This ablation event produces a transient, highly luminous plasma plume that expands rapidly away from the target surface. The plume created during the laser ablation process is highly forward directed and consists of mixture of energetic species including atoms, molecules, electrons, ions, clusters; micron sized solid particulates and molten globules. The ablated material is collected on a substrate mounted on the heater upon which it condenses resulting in the formation of quantum structures or the bulk like thin films depending upon the time and other conditions of deposition.
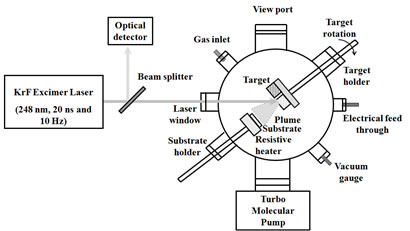
Schematic of PLD setup including vacuum chamber and KrF (248 nm) excimer laser

Image of PLD setup at ONEL, LMPD consisting of KrF excimer laser and PLD chambers.
|
|
















